06 Nov Automated validation of QR codes
QR code or Quick Response code is a two-dimensional barcode invented in 1994 by a Japanese company Denso Wave for labelling automobile parts. It normally contains black squares on a white background and is readable by image scanners. It may include custom data specific to a product.
Role of QR codes in advertising
- Linking users to detailed product/service information so that they can make informed decisions.
- Navigating users to the product/service page where they can make a purchase.
- Allowing users to download apps on their phones. Apps can then be used for information and
purchase events. - Offering discount coupons using QR codes to nudge users for a purchase.
Following are some of the common types of video advertisements (Ads):
TV ads
Traditionally, the main objective of TV ads was to build brand awareness. However, currently, they are also designed to achieve conversions by displaying QR codes to the users. The usage of QR codes adds immense power with increased conversions, leading to much higher ROI for brand owners.
Internet/Social media ads
Social media and Internet video ads are normally contextual and usually designed for conversions. QR
codes are an excellent tool to achieve conversions, especially with the usage of mobile devices as the
primary source of interaction and transactions.
Infomercials
Infomercials (teleshopping) are long-form television or online advertisements to pitch goods or services with a clear call-to-action. They are persuasive and can present more detailed information about the product with a clear aim for users to make a purchase. QR codes are frequently used in Infomercials to provide more product information or a direct purchase link. It is therefore obvious that QR codes are extremely useful in ads for brand owners to drive conversions.
Imagine, what would happen if:
- A user scans the QR code and nothing happens!
- User is taken to the wrong product
- User is taken to an invalid website URL that doesn’t work
- User is trying to download the app and the app URL is incorrect
All the above scenarios will frustrate the user and he will likely reject the brand straight away. This will have a detrimental effect on the brand investment – both in the short-term and long term. Many times, the life span of a promo video is too small and may lead to significantly missing the commercial opportunity for the brand owners. The entire campaign can be dysfunctional with the usage of faulty QR codes.
QR code validation requirements
Multiple things can go wrong while implementing QR codes in your advertising content.
- Incorrect QR code placement.QR codes may need to be placed in a specific area of the video so as not to obstruct the main ad content while still keeping it easy for users to locate and interact with. Some advertisers may want to keep a fixed location such as lower third while others may depend on the ad content.
- Unreadable QR code. QR code may be visible but it may be too small or coded with poor quality making it unusable by common mobile scanners.
- No URL in the QR code. Advertisers may want to embed a URL within the QR code for user interaction. It may sometimes happen that there is no URL coded inside the QR code.
- Incorrect URL. The URL may be present in the QR code but it may not be syntactically valid. Or it may be syntactically valid but not accessible. Both these scenarios render the URL useless for interaction.
Ways to validate QR code
QR code may be present through the ad content or only at specific locations. One of the ways to validate the QR code is manual QC. In that case, an operator will have to manually find the spots where the QR code is showing and then perform manual testing with mobile scanners to validate if the QR code is working as expected. Consider an Ad aggregator who delivers 1 million ad spots a year. Is it possible for such an organization to resort to manual validation of QR codes? If an organization is even delivering 100K ad assets a year, it is still impossible for them to manually validate all the QR code locations in all Ad spots.
The only practical answer to effectively perform this validation is the Automated QC (AQC). By using an Automated QC tool, users can configure what they need to check and where. AQC systems can quickly perform detection, parsing and validation of QR codes found in the ad content.
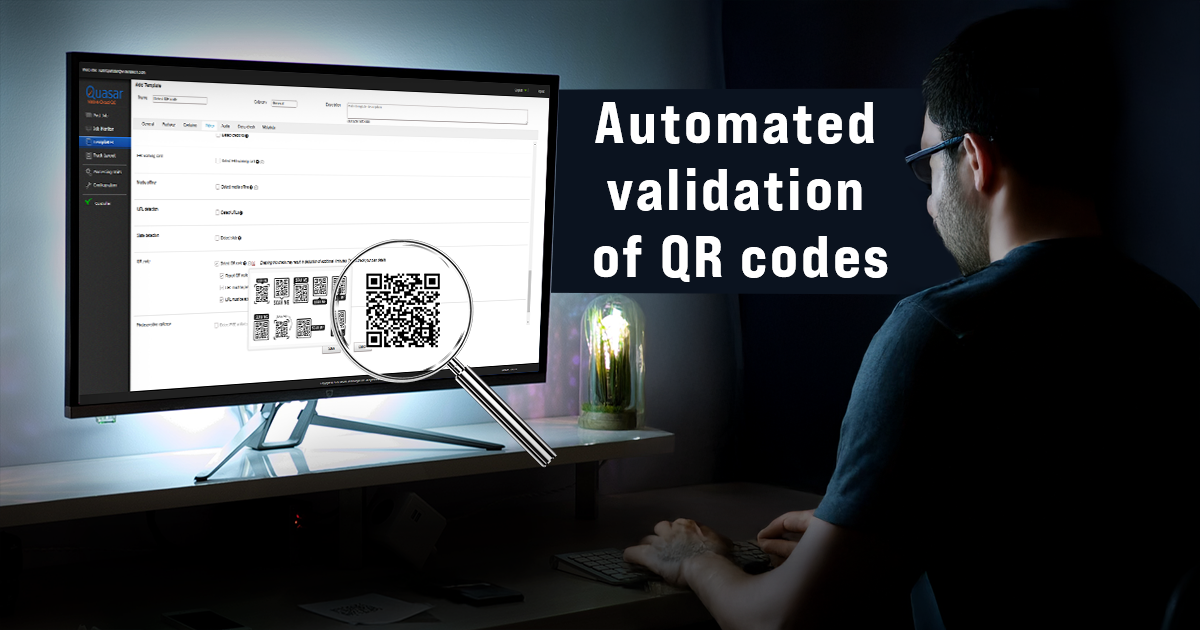
How can Quasar help?
Quasar is a highly scalable, cloud-native Automated file QC system, designed to automate the validation of a large number of Ad assets quickly. It has the following capabilities for QR code validation:
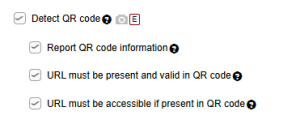
- Check for the QR code presence in the content. If it is present, Quasar will report the specific timecode locations of all segments with a QR code.
- Parse the information in the QR code and report it in a human-readable format. This can be helpful and efficient for an operator to review the correctness of information.
- Validate if the URL format is valid in the QR code.
- Validate if the URL in the QR code is accessible.
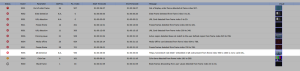
The QC results are reported in XML, JSON and PDF formats. Following is an example of the reported QR code information:
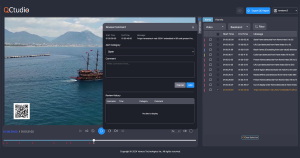
QCtudio review & collaboration system can be used to review the violations directly on a video timeline.
During review, users can also add comments and collaborate with other stakeholders to either rectify the content, accept or reject it.
Conclusion
Automated QC with an efficient review is more viable for addressing QR codes, especially in a large content volume environment. Quasar can perform Automated QC of large content volumes and can be integrated with orchestration systems to trigger callbacks on success or failure conditions. Orchestration systems can pull the QC reports produced by Quasar and use them for downstream workflow actions.
QCtudio then allows operators to quickly review the results while collaborating with all stakeholders to ensure swift content decisions.
With an end-to-end QC workflow toolset, Venera provides an integrated environment facilitating highly efficient content verification.